System Safety Engineering Process Workflow
Connecting The Reliability and Safety Engineering Artifacts (FMEA, FMECA & FTA)
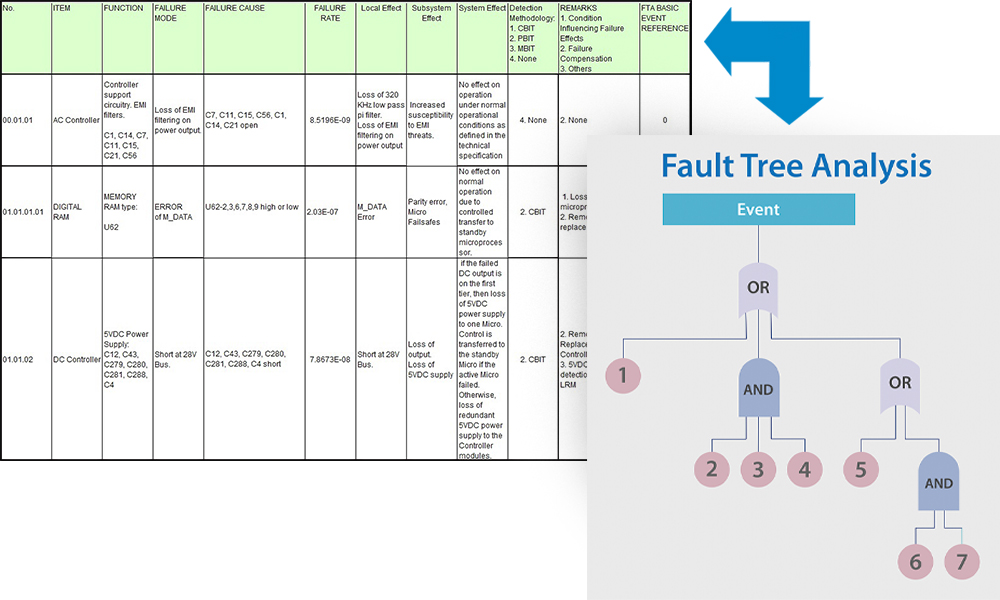
FTA basic events are linked to the FMEA Identifications and Effect Descriptions to establish traceability between the Reliability Engineering artifacts (example: FMEA, FMECA, e.t.c) and System Safety Engineering artifacts (example: FTA).
Dansob System Safety Engineering Process Flow accomplishes the following objectives:
- Help our customers build a safe and reliable products.
- Ensures our Product or System Safety Engineering key metric attribute (failure probability) satisfies our customers Safety Objective Requirement Specifications.
System Safety Assessment (SSA):
Is a safety evaluation of a system or process to assess compliance with specified safety objective requirements. SSA entails qualitative and quantitative evaluation methodologies.
SSA Elements:
Preliminary Hazard List (PHL):
Is a preliminary lists of failure hazards specified for safety risk evaluations or assessments.
Failure hazard list are categorized into the following severity levels: Catastrophic, Critical (or Hazardous), Major, Minor and No Safety Effect.
System Functional Hazard Analyses (SFHA):
Is a well-defined, quantitative analysis of a system safety process with the intent to identify and categorize potential failure hazards associated with the operation of the proposed system or process.
Also, SFHA failure hazards are categorized into the following severity levels: Catastrophic, Critical (or Hazardous), Major, Minor and No Safety Effect.

Design Assurance Level (DAL):
Determines the rigor of complex product development and their verification activities. It also emphasizes the safety aspects of the hardware and software elements of a product development process based on the severity of their functionalities and implementations.
DAL designations are based on the effects, severities and safety impact assessment of the complex product functionalities.
DAL designations are decomposed as follow:
- Functional Design Assurance Level (FDAL) – entails complex software DAL assessment.
- Item Design Assurance Level (IDAL) – entails complex hardware DAL assessment.
DAL designation flows from A to E.
DAL A denotes the most stringent DAL assignment based on highest severity and safety impact assessment (example: applied to safety-critical product failures that would cause or result in catastrophic hazards).
DAL E denotes the least stringent DAL assignment based on lowest severity and safety impact assessment (example: applied to non safety-critical product failures that would cause or result in no system effects).
DAL conforms with the guidelines of ARP4754 specification standards.
Design Assurance Level (DAL):
Assesses the safety impact of identified safety-critical common mode failures within a product design or system.
It is highly desirable to inhibit inherent common mode failures of a safety-critical system.
It is also highly desirable to establish and maintain separation and independence of safety-critical systems.
Zonal Safety Analyses (ZSA):
Entails the identification and mitigation of fire hazard risks within a product design or fire hazard risk zones within a system.
Examples:
- Lamination of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) with fire resistant (or suppressant) coatings (example: FR4 resin binder).
- Incorporating fire extinguishers in fire risk zones.
- Inserting an electronic Line Replaceable Unit (LRU) or Line Replaceable Module (LRM) into fire resistant enclosures.
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA):
Is a quantitative analysis that utilizes top-down approach and Boolean logic operation to evaluate the probability of an undesired (or unsafe) event.
Equations:
Failure Rate Function = ʎ𝑒−ʎ𝑡
Probability Density Function = ∫0𝑡 ʎ𝑒−ʎ𝑡 𝑑𝑡
Notes:
- Probability density function is also known as Failure Probability or Probability of Failure.
- ʎ denotes failure rate (per hour or per million hours).
- t denotes time (in hours).
- Failure Probability is evaluated for all PHL and SFHA derived failure hazards.
- PHL and SFHA derived failure hazards becomes (or represents) undesired top events of an FTA.
- Failure Probability are verified for compliance demonstration with the specified Safety Objective requirements.
- Safety Objective requirements are specified for failure hazard severities (or severity categories).
- Safety Objective requirements are referenced in the ARP4761 and MIL-STD-882E specification standards.
- ARP4761 standard is utilized for Commercial Applications.
- MIL-STD-882E standard is utilized for Military Applications

Safety Specification Standards and Regulations

- MIL-STD-882E
- ARP4754 - Aerospace Recommended Practice (ARP) Guidelines for the Development of Civil Aircraft and Systems.
- ARP4761 - ARP Guidelines for Conducting the Safety Assessment Process on Civil Aircraft, Systems and Equipment.
- DO-178C - Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification.
- DO-254 - Design Assurance Guidance for Airborne Electronic Hardware
Secure Your Systems with Dansob
Contact us today to learn how can we help implement or improve System Safety for your complex systems to ensure avoidance of critical system failures.